Launch of Common Good Cyber Workshop Report: Mitigating the Systemic Underfunding of Cybersecurity Nonprofits
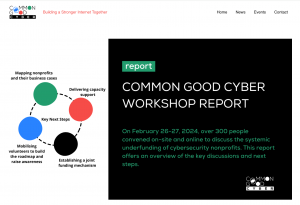
The Common Good Cyber initiative, a collaborative effort aimed at addressing the challenge of sustaining nonprofit and public interest organizations involved in critical cybersecurity functions, announces the release of its workshop report. The report encapsulates insights and outcomes from a landmark gathering held in February 2024 at the National Press Club in Washington, D.C., United States.
The workshop, jointly organized by leading cybersecurity organizations including the Cyber Threat Alliance, the CyberPeace Institute, the Forum of Incident Response and Security Teams (FIRST), the Global Cyber Alliance, the Institute for Security and Technology (IST), and the Shadowserver Foundation, convened over 100 stakeholders representing various sectors including government, multilateral organizations, civil society, foundations, business, and academia. An additional 200 participants joined online to discuss the systemic underfunding of cybersecurity nonprofits and explore sustainable funding approaches.